- Processes
- Polymer Processing
- Blow Molding
- Injection Molding
- Metal Injection Molding
- Thermoforming
- Metal Casting
- Centrifugal Casting
- Die Casting
- Investment Casting
- Permanent Mold
- Sand Casting
- Shell Mold Casting
- Machining
- Milling
- Turning
- Hole-making
- Drill Size Chart
- Tap Size Chart
- Sheet Metal Fabrication
- Forming
- Cutting with shear
- Cutting without shear
- Gauge Size Chart
- Additive Fabrication
- SLA
- FDM
- SLS
- DMLS
- 3D Printing
- Inkjet Printing
- Jetted Photopolymer
- LOM
- Materials
- Metals
- Plastics
- Case Studies
- Cost Analysis
- Part Redesign
- Product Development
- Resources
- Curriculum Resources
- Glossary
Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS)
was developed jointly by Rapid Product Innovations (RPI)
and EOS GmbH, starting in 1994, as the first commercial
rapid prototyping method to produce metal parts in a
single process. With DMLS, metal powder (20 micron
diameter), free of binder or fluxing agent, is
completely melted by the scanning of a high power laser
beam to build the part with properties of the original
material. Eliminating the polymer binder avoids the
burn-off and infiltration steps, and produces a 95%
dense steel part compared to roughly 70% density with
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS). An additional benefit
of the DMLS process compared to SLS is higher detail
resolution due to the use of thinner layers, enabled by
a smaller powder diameter. This capability allows for
more intricate part shapes. Material options that are
currently offered include alloy steel, stainless steel,
tool steel, aluminum, bronze, cobalt-chrome, and
titanium. In addition to functional prototypes, DMLS is
often used to produce rapid tooling, medical implants,
and aerospace parts for high heat applications.
The DMLS process can be performed
by two different methods, powder deposition and powder
bed, which differ in the way each layer of powder is
applied. In the powder deposition method, the metal
powder is contained in a hopper that melts the powder
and deposits a thin layer onto the build platform. In
the powder bed method (shown below), the powder
dispenser piston raises the powder supply and then a
recoater arm distributes a layer of powder onto the
powder bed. A laser then sinters the layer of powder
metal. In both methods, after a layer is built the build
piston lowers the build platform and the next layer of
powder is applied. The powder deposition method offers
the advantage of using more than one material, each in
its own hopper. The powder bed method is limited to only one
material but offers faster build speeds.
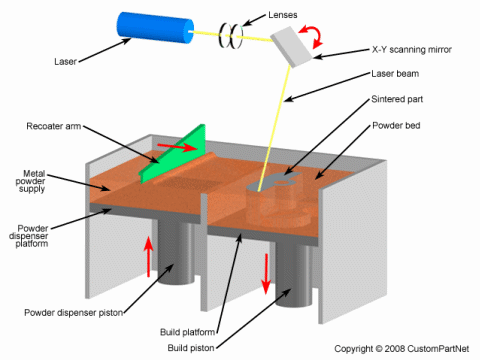
Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS)
Capabilities
Disclaimer: All process specifications reflect the approximate range of a process's capabilities and should be viewed only as a guide. Actual capabilities are dependent upon the manufacturer, equipment, material, and part requirements.
Return to top |