- Processes
- Polymer Processing
- Blow Molding
- Injection Molding
- Metal Injection Molding
- Thermoforming
- Metal Casting
- Centrifugal Casting
- Die Casting
- Investment Casting
- Permanent Mold
- Sand Casting
- Shell Mold Casting
- Machining
- Milling
- Turning
- Hole-making
- Drill Size Chart
- Tap Size Chart
- Sheet Metal Fabrication
- Forming
- Cutting with shear
- Cutting without shear
- Gauge Size Chart
- Additive Fabrication
- SLA
- FDM
- SLS
- DMLS
- 3D Printing
- Inkjet Printing
- Jetted Photopolymer
- LOM
- Materials
- Metals
- Plastics
- Case Studies
- Cost Analysis
- Part Redesign
- Product Development
- Resources
- Curriculum Resources
- Glossary
The first commercial Laminated Object Manufacturing (LOM) system was shipped in 1991. LOM was developed by Helisys of Torrance, CA. The main components of the system are a feed mechanism that advances a sheet over a build platform, a heated roller to apply pressure to bond the sheet to the layer below, and a laser to cut the outline of the part in each sheet layer. Parts are produced by stacking, bonding, and cutting layers of adhesive-coated sheet material on top of the previous one. A laser cuts the outline of the part into each layer. After each cut is completed, the platform lowers by a depth equal to the sheet thickness (typically 0.002-0.020 in), and another sheet is advanced on top of the previously deposited layers. The platform then rises slightly and the heated roller applies pressure to bond the new layer. The laser cuts the outline and the process is repeated until the part is completed. After a layer is cut, the extra material remains in place to support the part during build.
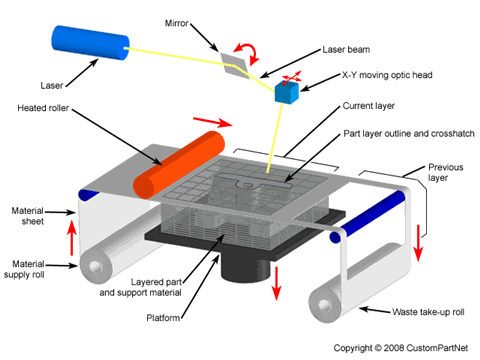
Laminated Object Manufacturing (LOM)
Capabilities
Disclaimer: All process specifications reflect the approximate range of a process's capabilities and should be viewed only as a guide. Actual capabilities are dependent upon the manufacturer, equipment, material, and part requirements.
Return to top |